Just like in Windows, you can have hidden files and directories are present in Linux systems. These are files that exist in the directory structure but cannot be seen without special options to commands. So, this is how to show hidden files in Ubuntu and Other Linux systems.
When you are in the terminal of your Ubuntu system you can use the ls command to list the files in your current directory. Using this command as is will show a list of files and directories excluding the hidden ones. To show the hidden files use this command.
$ ls -aIn the output, the hidden files and folders will be denoted by the dot (.) before their names.
myuser@ubuntu:/$ ls -a
. bin dev home lib32 libx32 media opt root sbin srv tmp var
.. boot etc lib lib64 lost+found mnt proc run snap sys usr
myuser@ubuntu:/$If you use Ubuntu or other similar Desktop Linux, you can still see the hidden files and directories. This can be done by opening the File Manager then using the “Ctrl+H” keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu.
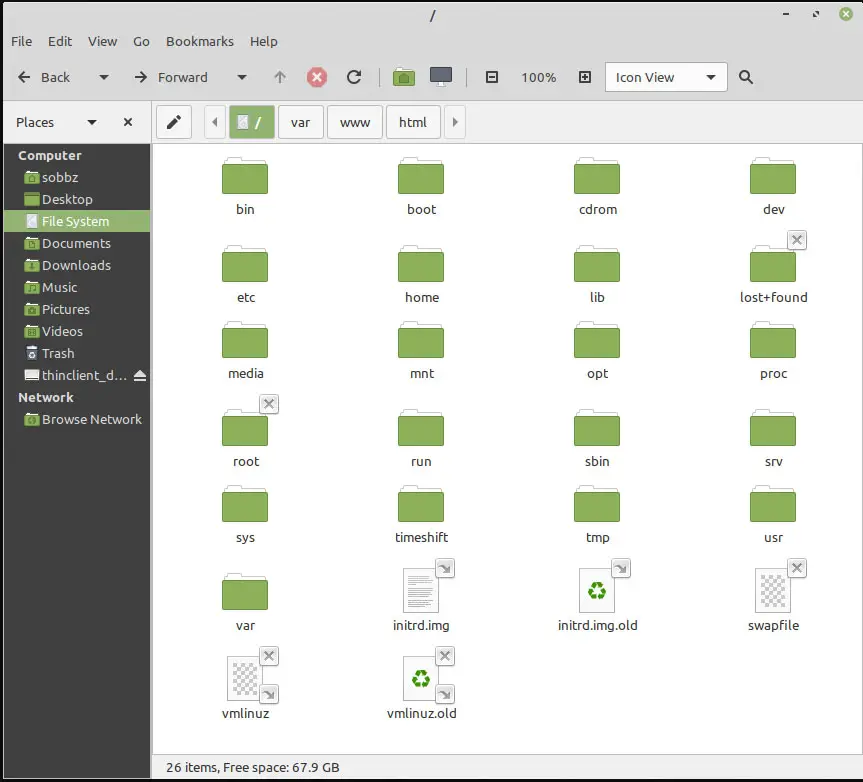
The “Ctrl+H” keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu will toggle the visibility of the hidden files and directories therefore the same command can be used to hide hidden files in Ubuntu.
How to hide files or folders in Ubuntu
To hide a file or folder in Ubuntu is quite simple. Just rename the target file by prepending a dot before its file name.
Example:
$ sudo mv myfile .myfileOn Linux Desktop, right-click on the file or directory icon and choose the rename option, then add the dot before the name.
Bonus: Show Hidden Files in Ubuntu in Bulk
if you create a .hidden file and add the names of the directories in this file, those directories will be hidden from view when you close your file manager and open it again. This is true only for objects within the current directory and will not propagate to other sub-directories.
Found this article interesting? Follow Brightwhiz on Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube to read and watch more content we post.